大模型'手脚'延伸:深入解析AI工具调用与智能体进化之路
鱼雪的AI博客-来自NotebookLM
目录
引言
随着大语言模型(LLM)技术的快速发展,单纯的文本生成已经无法满足复杂应用场景的需求。**工具调用(Tool Calling)**作为一种重要的扩展机制,让大模型能够与外部系统交互,获取实时数据,执行特定任务,从而构建更加智能和实用的 AI 应用。
本文将深入探讨大模型工具调用的核心原理,并通过一个完整的 Rust 项目案例,详细讲解如何实现一个支持天气查询和网络搜索的智能助手,使用原生的HTTP调用方式,不使用任何第三方LLM服务的客户端,比如Python的openai库,这样便于对原理有更清晰的理解,也便于根据任何编程语言开发自己工具,而不局限于特定库。
大模型工具调用算是LLM中一种动态获取,或说实时获取与用户提问相关数据的一种方式,为用户的问题提供可靠的上下文。另外一种方式基于RAG的方式,这种是基于知识库,更像是一种静态知识。之后会用别的文章再来讨论,敬请期待。
关键词
- 大语言模型 (Large Language Model, LLM)
- 工具调用 (Tool Calling)
- Function Calling
- AI Agent
- Rust 异步编程
- DeepSeek API
大模型工具调用基础原理
什么是工具调用?
LLM 工具调用是指大语言模型在生成回答时,能够识别用户需求并主动调用预定义的外部函数或 API 来获取信息或执行操作的能力。这种机制让 LLM 从纯文本生成器转变为能够与现实世界交互的智能代理。
核心优势
- 实时性:获取最新的数据和信息
- 准确性:避免模型幻觉,提供可靠的事实信息
- 扩展性:通过工具扩展模型能力边界
- 可控性:明确的函数调用过程,便于调试和监控
工具调用流程详解
完整流程图
---
id: f662e516-56f0-46a1-a622-1438ab60949c
---
sequenceDiagram
participant User as 用户
participant App as 应用程序
participant LLM as 大语言模型
participant Tool as 外部工具/API
User->>App: 发送查询请求
App->>LLM: 用户请求 + 工具函数描述(JSON对象)
LLM->>App: 选�择的工具函数 + 工具调用参数
App->>Tool: 匹配实际工具函数填充参数并调用
Tool->>App: 获取实际工具函数执行结果
App->>LLM: 用户请求 + 工具函数执行结果
LLM->>App: 生成最终回答
App->>User: 返回完整回答
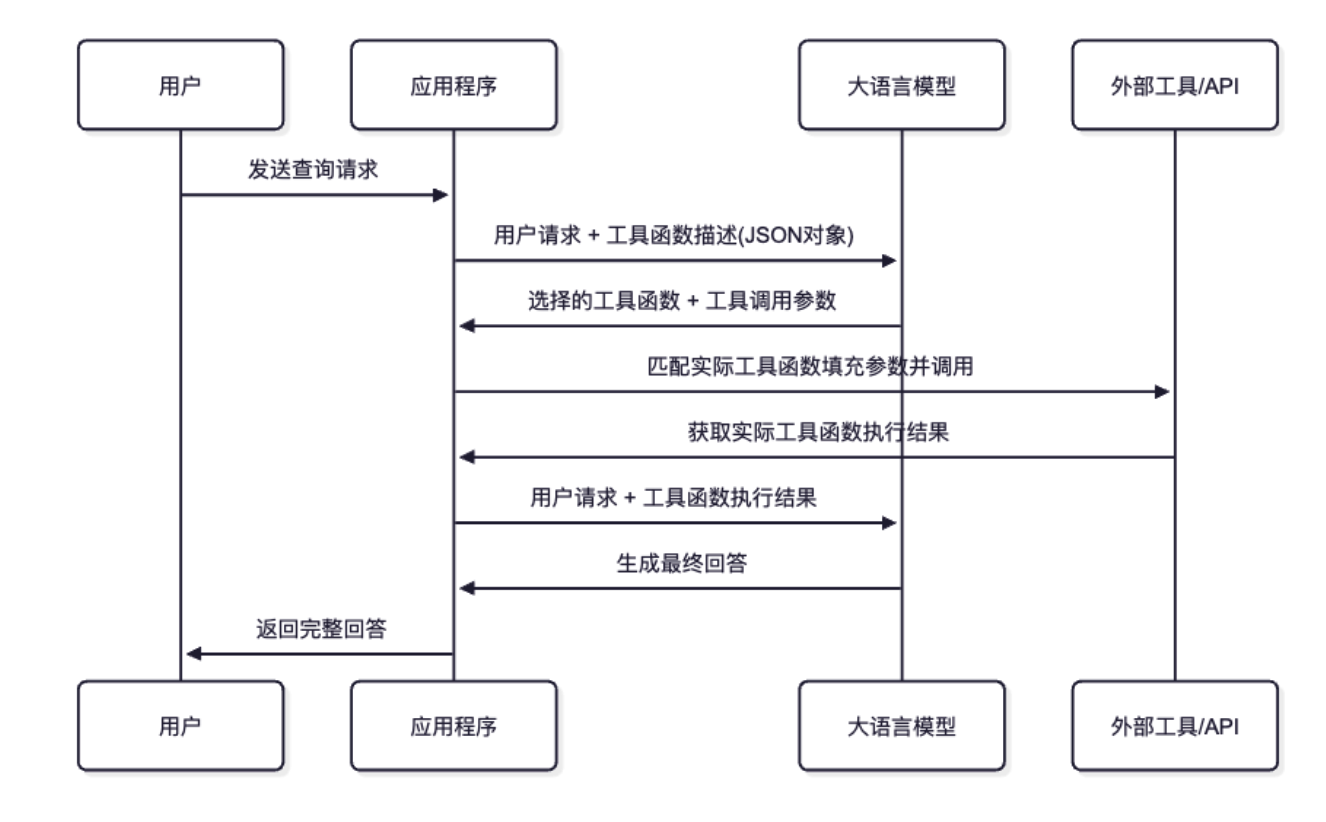
详细步骤分析
1. 初始请求阶段
用户向系统发送查询请求,应用程序将请求连同预定义的函数工具描述一起发送给大模型。
{
"model": "deepseek-chat",
"messages": [
{
"role": "system",
"content": "你是一个专业的助手,可以提供天气信息和搜索功能"
},
{
"role": "user",
"content": "今天上海的天气怎么样?"
}
],
"tools": [
{
"type": "function",
"function": {
"name": "get_weather",
"description": "获取指定城市的天气预报信息",
"parameters": {
"type": "object",
"properties": {
"location": {
"type": "string",
"description": "城市名称"
}
},
"required": ["location"]
}
}
}
],
"tool_choice": "auto"
}
2. 模型决策阶段
大模型分析用户请求,识别(根据工具的描述文档,然后自行决定调用需要调用哪些工具)出需要调用天气查询工具,并返回结构化的工具�调用指令(函数名 + 与之匹配的参数):
{
"choices": [
{
"message": {
"role": "assistant",
"content": null,
"tool_calls": [
{
"id": "call_123",
"type": "function",
"function": {
"name": "get_weather",
"arguments": "{\"location\": \"上海\"}"
}
}
]
}
}
]
}
3. 工具执行阶段
应用程序解析工具调用指令,执行��实际的 API 调用:
// 解析工具调用参数
let args: Value = serde_json::from_str(
call["function"]["arguments"].as_str().unwrap()
)?;
let location = args["location"].as_str().unwrap();
// 调用实际的天气 API
let weather_info = amap::get_weather(location, &amap_key).await?;
4. 结果整合阶段
将工具执行结果反馈给大模型,生成最终的用户友好回答:
{
"model": "deepseek-chat",
"messages": [
{
"role": "system",
"content": "你是一个专业的天气顾问,请根据天气数据给出详细建议"
},
{
"role": "assistant",
"content": null,
"tool_calls": [...]
},
{
"role": "tool",
"content": "天气数据JSON",
"tool_call_id": "call_123"
}
]
}
Rust 实现案例分析
项目架构概览
我们的项目采用模块化设计,主要包含以下组件:
src/
├── main.rs # 主程序入口和聊天逻辑
├── tools/ # 工具模块
│ ├── mod.rs # 工具注册和统一接口
│ ├── amap.rs # 高德天气 API 工具
│ └── serper.rs # Google 搜索 API 工具
核心代码实现
1. 主聊天逻辑
async fn chat(user_query: &str) -> Result<(), Box<dyn std::error::Error>> {
let api_key = env::var("DEEPSEEK_API_KEY").unwrap();
let endpoint = env::var("DEEPSEEK_API_URL").unwrap();
// 构建包含工具定义的请求
let body = json!({
"model": env::var("MODEL_NAME").unwrap(),
"messages": [
{
"role": "system",
"content": "你是一个专业的助手,可以提供天气信息和搜索功能"
},
{"role": "user", "content": user_query}
],
"tools": get_tools_definition(),
"tool_choice": "auto", // 使用`auto`让大模型自行决定使用哪些工具
});
// 发送初始请求
let response = reqwest::Client::new()
.post(&endpoint)
.header("Authorization", format!("Bearer {}", api_key))
.json(&body)
.send()
.await?
.json::<Value>()
.await?;
// 处理工具调用
if let Some(tool_calls) = response["choices"][0]["message"]["tool_calls"].as_array() {
for call in tool_calls {
let tool_result = handle_tool_call(call).await?;
// 将结果反馈给�模型生成最终回答
let final_response = generate_final_response(&api_key, &endpoint, call, &tool_result).await?;
info!("最终回答: {}", final_response["choices"][0]["message"]["content"]);
}
}
Ok(())
}
2. 工具注册系统
为了实现高内聚、低耦合的设计,我们创建了一个统一的工具注册系统:
// 工具处理结果结构
pub struct ToolResult {
pub content: String,
pub system_prompt: String,
}
// 工具处理函数类型
type ToolHandler = Box<dyn Fn(&Value) -> Pin<Box<dyn Future<Output = Result<ToolResult, Box<dyn std::error::Error>>> + Send + Sync>> + Send + Sync>;
// 工具注册表
struct ToolRegistry {
tools: HashMap<String, ToolHandler>,
}
impl ToolRegistry {
fn new() -> Self {
let mut tools = HashMap::new();
// 注册天气查询工具
let weather_handler: ToolHandler = Box::new(|call: &Value| {
let call = call.clone();
Box::pin(async move {
let args: Value = serde_json::from_str(call["function"]["arguments"].as_str().unwrap())?;
let location = args["location"].as_str().unwrap();
let amap_key = env::var("AMAP_API_KEY").unwrap();
let weather_info = amap::get_weather(location, &amap_key).await?;
Ok(ToolResult {
content: serde_json::to_string(&weather_info)?,
system_prompt: "�你是一个专业的天气顾问,请根据获取到的天气数据给出详细的穿衣建议".to_string(),
})
})
});
tools.insert("get_weather".to_string(), weather_handler);
// 注册搜索工具
let search_handler: ToolHandler = Box::new(|call: &Value| {
let call = call.clone();
Box::pin(async move {
let args: Value = serde_json::from_str(call["function"]["arguments"].as_str().unwrap())?;
let query = args["query"].as_str().unwrap();
let search_results = serper::search(query).await?;
let formatted_results = serper::format_results(&search_results, 3);
Ok(ToolResult {
content: formatted_results,
system_prompt: "你是一个专业的信息分析师,请根据搜索结果给出准确、简洁的回答".to_string(),
})
})
});
tools.insert("search".to_string(), search_handler);
Self { tools }
}
}
// 统一的工具调用处理函数
pub async fn handle_tool_call(call: &Value) -> Result<ToolResult, Box<dyn std::error::Error>> {
let tool_name = call["function"]["name"].as_str().ok_or("无效的工具名称")?;
let registry = get_registry();
match registry.get_handler(tool_name) {
Some(handler) => handler(call).await,
None => Err(format!("未知的工具调用: {}", tool_name).into()),
}
}
3. 天气查询工具实�现
pub async fn get_weather(location: &str, api_key: &str) -> Result<WeatherResponse, reqwest::Error> {
// 第一步:获取城市行政编码
let district_url = format!(
"https://restapi.amap.com/v3/config/district?key={}&keywords={}&subdistrict=0&extensions=all",
api_key, location
);
let district_resp: DistrictResponse = reqwest::get(&district_url).await?.json().await?;
if district_resp.status != "1" || district_resp.districts.is_empty() {
return Err(reqwest::get("http://error").await.unwrap_err());
}
let adcode = &district_resp.districts[0].adcode;
// 第二步:获取天气数据
let weather_url = format!(
"https://restapi.amap.com/v3/weather/weatherInfo?key={}&city={}&extensions=all&output=json",
api_key, adcode
);
let weather_resp: WeatherResponse = reqwest::get(&weather_url).await?.json().await?;
if weather_resp.status != "1" {
return Err(reqwest::get("http://error").await.unwrap_err());
}
Ok(weather_resp)
}
4. 搜索工具实现
pub async fn search(query: &str) -> Result<Vec<SearchResult>, reqwest::Error> {
let api_key = env::var("SERPER_API_KEY").expect("SERPER_API_KEY must be set");
let client = reqwest::Client::new();
let response = client
.post("https://google.serper.dev/search")
.header("X-API-KEY", api_key)
.header("Content-Type", "application/json")
.json(&serde_json::json!({
"q": query,
"type": "search"
}))
.send()
.await?
.json::<SearchResponse>()
.await?;
let results = response
.organic
.into_iter()
.map(|result| SearchResult {
title: result.title,
link: result.link,
snippet: result.snippet,
})
.collect();
Ok(results)
}
pub fn format_results(results: &[SearchResult], max_results: usize) -> String {
let results = results
.iter()
.take(max_results)
.enumerate()
.map(|(i, result)| {
format!(
"{}. {}\n 链接: {}\n 摘要: {}\n",
i + 1,
result.title,
result.link,
result.snippet
)
})
.collect::<Vec<_>>()
.join("\n");
if results.is_empty() {
"没有找到相关结果。".to_string()
} else {
results
}
}
代码架构设计
设计原则
我们的实现遵循以下软件设计原则:
- 高内聚:相关功能集中在同一模块中
- 低耦合:模块间依赖关系最小化
- 模块化:清晰的模块边界和职责分离
- 可扩展性:易于添加新的工具和功能
模块职责划分
- main.rs:负责主程序逻辑和 LLM 交互
- tools/mod.rs:工具注册表和统一接口
- tools/amap.rs:天气查询功能实现
- tools/serper.rs:搜索功能实现
异步编程模式
项目大量使用 Rust 的异步编程特性:
// 使用 tokio 运行时
#[tokio::main]
async fn main() -> Result<(), Box<dyn std::error::Error>> {
// 异步函数调用
chat(user_query).await?;
Ok(())
}
// 异步工具处理函数
type ToolHandler = Box<dyn Fn(&Value) -> Pin<Box<dyn Future<Output = Result<ToolResult, Box<dyn std::error::Error>>> + Send + Sync>> + Send + Sync>;
最佳实践与优化
1. 错误处理
使用 Rust 的 Result 类型进行优雅的错误处理:
pub async fn handle_tool_call(call: &Value) -> Result<ToolResult, Box<dyn std::error::Error>> {
let tool_name = call["function"]["name"].as_str().ok_or("无效的工具名称")?;
// ... 其他逻辑
}
2. 环境变量管理
使用 dotenv 管理敏感配置:
use dotenv::dotenv;
#[tokio::main]
async fn main() -> Result<(), Box<dyn std::error::Error>> {
dotenv().ok();
let api_key = env::var("DEEPSEEK_API_KEY").unwrap();
// ...
}
3. 日志记录
使用 tracing 进行结构化日志记录:
use tracing::{Level, info};
info!("用户查询: {}", user_query);
info!("工具调用参数: {}", serde_json::to_string_pretty(&args).unwrap());
4. 性能优化
- 使用连接池复用 HTTP 连接
- 实现请求缓存机制
- 并发处理多个工具调用
5. 安全考虑
- API 密钥安全存储
- 输入参数验证
- 请求频率限制
扩展功能建议
1. 添加更多工具
// 数据库查询工具
let db_handler: ToolHandler = Box::new(|call: &Value| {
// 数据库查询逻辑
});
// 文件操作工具
let file_handler: ToolHandler = Box::new(|call: &Value| {
// 文件操作逻辑
});
2. 实现工具链
支持多个工具的串联调用,实现复杂的业务流程。
3. 添加缓存机制
use std::collections::HashMap;
use std::sync::Arc;
use tokio::sync::Mutex;
struct CacheManager {
cache: Arc<Mutex<HashMap<String, String>>>,
}
4. 监控和指标
添加工具调用的性能监控和成功率统计。
总结
大模型工具调用是构建智能 AI 应用的关键技术。通过本文的详细分析,我们了解了:
- 工具调用的基本原理:从用户请求到最终回答的完整流程
- 实现架构设计:模块化、可扩展的代码组织方式
- 具体代码实现:使用 Rust 构建高性能的工具调用系统
- 最佳实践:错误处理、日志记录、性能优化等方面的建议
这种架构不仅提供了良好的代码组织结构,还为后续功能扩展奠定了坚实基础。随着大模型技术的不断发展,工具调用将成为构建复杂 AI 应用的标准模式。
相关资源
本文展示了如何使用 Rust 构建支持工具调用的大模型应用。如果您对实现细节有疑问,欢迎查看完整的项目源码或提出 Issue 讨论。